Welding
Welding: Creating connections and shaping metals
Welding
Welding: Basics and techniques
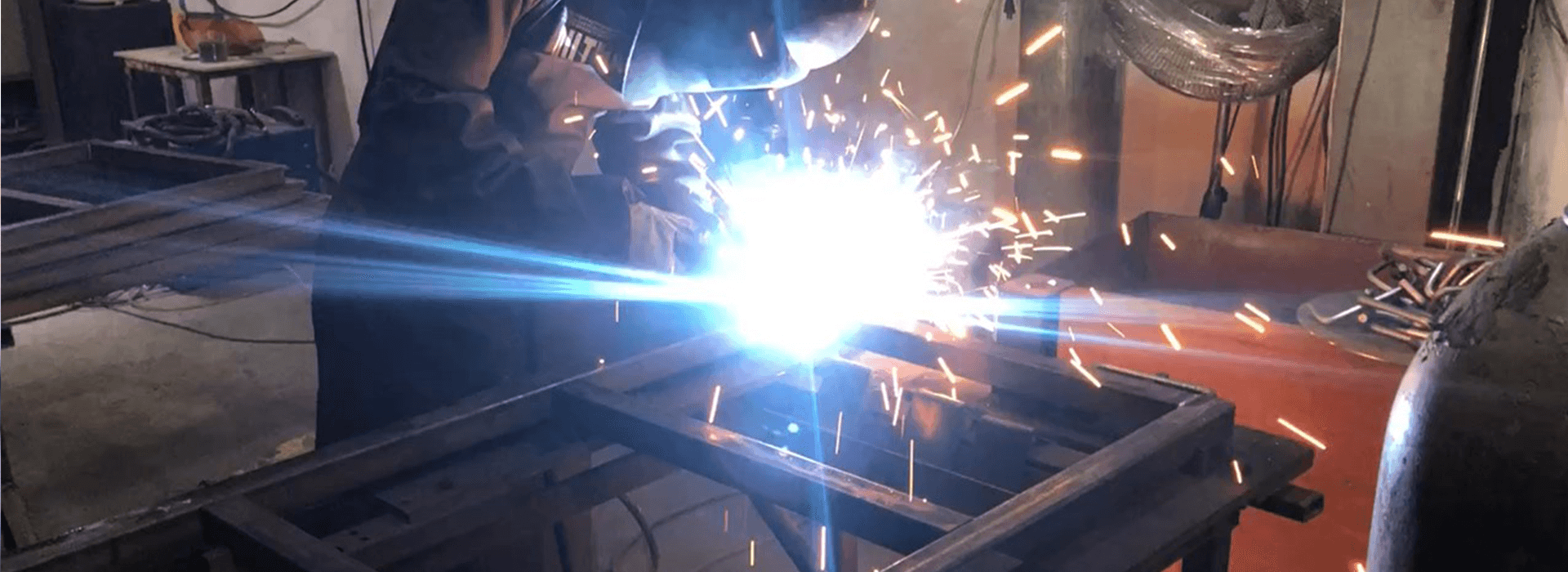
Welding is a manufacturing process in which materials are joined using heat, pressure or a combination of both. In welding, the materials are heated to melting at the junction to join the parts and create a strong connection to promote. Often, a filler material is added during welding to form a weld seam that creates a strong connection between the workpieces after cooling. In addition, shielding gases or a vacuum can be used to prevent oxidation or other impurities in the weld area. There are various welding techniques that depend on the material, application and desired strength of the connection can be selected. The most common welding processes include: MIG welding or MAG welding, TIG welding, shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), spot welding and laser welding. In addition to the various welding processes, the degree of automation depends on the application of welding and can range from manual production, the fully automated welding to the robotic welding.
Welding - advantages & procedures
Welding: Insights into methodology and benefits
Advantages of welding at Line Up
Welding
MIG welding (metal inert gas welding)
MIG welding is a widely used welding method that is particularly characterized by high efficiency and good controllability. In MIG welding, a wire electrode that runs through a welding torch is continuously fed. In addition, MIG welding uses an inert gas such as argon or helium to protect the weld seam from atmospheric contamination and impurities. Since the gases do not react with the molten pool, a very clean weld seam can be achieved. MIG welding is particularly suitable for welding steel, stainless steel or aluminum and is often used in the manufacturing industry. The high welding speed and the ability to pull long weld seams without interruption make MIG welding a preferred choice for production environments.
MAG welding (metal active gas welding)
MAG welding is similar in welding process to MIG welding, but uses an active gas such as carbon dioxide or mixed gases that react with the molten pool. This method is particularly suitable for welding unalloyed or low-alloy steel and provides a cost-effective solution for many welding applications. Due to its high versatility, MAG welding is a valued manufacturing process.
TIG welding (tungsten inert gas welding)
TIG welding is known for its high precision and the ability to weld thin materials and metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, titanium and copper alloys. To stabilize the arc and protect the weld seam, this welding process uses a non-melting tungsten electrode and inert gas. The inert gas is typically argon or helium. TIG welding requires a high level of skill and is often used for very demanding welding work where the aesthetics and quality of the weld seam are of greater importance.
Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW)
One of the oldest and most widely used welding methods is shielded metal arc welding, which is often referred to as shielded metal arc welding with coated electrodes. The great advantage of this method is its flexibility, as no external gas cylinder is required. The shielding gas envelope comes directly from the introduced electrode when it burns. This welding method is particularly suitable for repair work and assembly work outdoors, as the welding process is less susceptible to wind and weather.
Spot welding
Spot welding is a resistance welding process. The metal parts are clamped between two electrodes. When the current is switched on, a high heat is generated due to the electrical resistance at the contact points of the metal. This heat is so intense that the metal melts and joins at these points. After the metal has cooled, a solid weld joint, or a weld spot, is formed. Spot welding is a cost-effective solution due to its simplicity and efficiency and is particularly often used in series production, where many fast and reliable connections are required.
Laser welding
Laser welding uses the energy of a highly focused laser beam to melt the workpieces and create a connection. This welding process offers a precise and clean weld seam with minimal heat input. Laser welding is ideal for very fine welding work, electronic components and detailed constructions. This is why this welding process is often used in medical technology, microelectronics or welding thin sensitive materials.
Metal processing - Inquiry
Line Up: Start your procurement process now
Make an inquiry
Receive offer
Place order
Receive products
Other manufacturing processes of metal processing
Realize your products with the metal processing of Line Up
Contact
Ready to Line Up?
Contact us!
Personally there for you throughout Europe and in China. When will you become one of our satisfied customers?