Table of Contents
11 Manufacturing processes in textile production
Reading Time: 9 min.

11 manufacturing processes in textile production that you should know
Every manufacturing process in textile production influences the quality, durability and functionality of the end product. We reveal which 11 processes you should know and how digitalisation is shaping textile processing.
Would you like to have clothing produced? Or are you planning to set up your own fashion label? Then you should have a basic understanding of the manufacturing processes used in the production of clothing and textiles.
Your advantage: you can make well-founded decisions, achieve the required functionality and ensure that the quality of the textiles produced leaves nothing to be desired.
How are fabrics made?
1. spinning
Spinning is the starting material for all further steps in textile processing. The fibres - whether cotton, wool, silk or synthetic materials such as polyester - are spun into yarns and later processed into textiles. The quality of the fabric is determined by the spinning process on the one hand and the strength and fineness of the yarn on the other.
Modern spinning techniques such as ring or rotor spinning have also significantly improved the efficiency and quality of yarn production, meaning that uniform, durable yarns can now be produced. Innovative spinning methods also make it possible to optimise fibre elongation, which has a positive effect on the comfort and durability of the clothing produced.
Areas of application: Clothing, home textiles and technical textiles,
Important processes: Ring spinning, rotor spinning and airjet spinning.
Technological developments: Automated spinning processes increase efficiency and enable more precise yarn production.
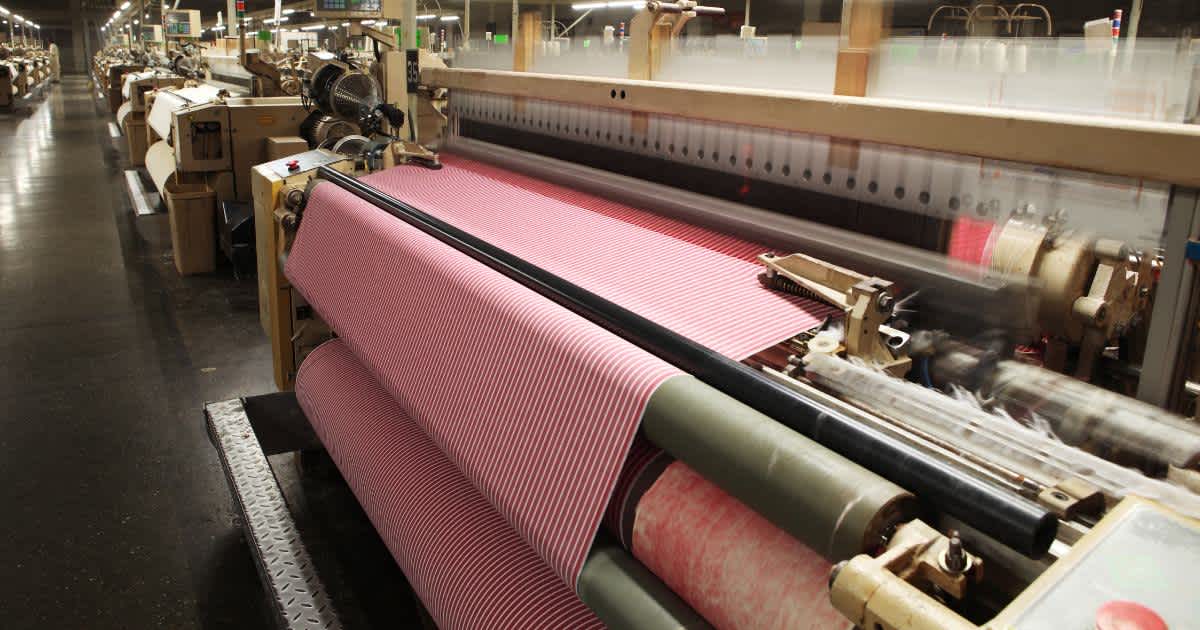
2. weaving
Weaving is one of the oldest manufacturing processes in textile production and requires the interaction of two yarn systems - the warp and weft threads - to create a stable fabric. The result is a fabric that has different strengths, structures and densities depending on the type of weave.
The choice of weave (e.g. plain, twill or satin weave) influences the appearance and functional properties of the fabric, such as flexibility and durability. Quality, on the other hand, is determined by factors such as weave density and yarn thickness, with the fineness of the weaving process playing a significant role. Modern textile machines enable precise and efficient processing and are indispensable in the production of industrial and technical textiles today.
Typical fabrics: denim, linen, satin and cotton.
Quality factors: Weave density, yarn thickness and weave type.
Advantage of structural diversity: Different weaves enable specific fabric properties such as breathability or stretchability.
3. knitting
Knitting differs fundamentally from weaving, as stitches are formed by interlacing yarns. This creates an elastic, often particularly soft fabric structure, which is ideal for flexible and comfortable clothing such as T-shirts, jumpers, sportswear and underwear.
The quality of the fabric is determined by the stitch structure, elasticity and yarn count. Modern knitting machines make it possible to produce highly complex patterns and designs that meet the high demands of the fashion industry. Knitting methods are also becoming increasingly environmentally friendly as they make the use of materials more efficient and minimise waste.
Areas of application: T-shirts, jumpers, underwear and sportswear.
Quality features: Elasticity, stitch structure and yarn count.
Machine knitting: Modern knitting machines enable high-precision and cost-efficient production of complex patterns.
4. colouring
Fabrics are dyed to create visual accents and characterise the textile design. The dyeing process involves a variety of techniques, such as reactive dyeing, pigment dyeing or garment dyeing, each of which achieves different effects and durability.
Today, sustainable dyeing processes are becoming increasingly important as they use less water and energy and therefore reduce the environmental impact. In addition, sustainable dyeing processes enable the use of environmentally friendly dyes with the aim of ensuring more environmentally friendly production. Innovative methods can also increase the colour brilliance and durability of textiles, which is particularly attractive for fashion labels.
Process: Reactive colouring, pigment colouring and acid colouring.
Trends: Sustainable colouring technologies and environmentally friendly dyes.
Colour brilliance: The technique used influences the durability and brilliance of the colours in the end product.
5. printing
Printing makes it possible to apply individual patterns, graphics and colours to textiles. Various processes such as screen printing, transfer printing or digital printing provide different design options for the clothing produced.
With digital printing, the designs are applied directly to the fabric, which is particularly flexible and enables complex patterns and colour transitions in the best quality thanks to the high precision. The use of water-saving digital printing technologies also saves resources, making the process attractive for particularly environmentally conscious brands. Durability and colour fastness are also important quality factors in printing to ensure long-lasting and visually appealing textiles.
Printing technologies: screen printing, transfer printing, sublimation printing and digital printing.
Quality: print durability, precision and colour fastness.
Sustainable options: Water-saving digital printing processes are increasingly environmentally friendly and reduce waste.
6. finishing
Finishing gives textiles additional properties that increase their quality and durability. For example, clothing can be given additional properties such as water repellency, anti-crease or anti-pilling functions through chemical and mechanical treatments. Finishing not only improves the durability of the fabric, but also its comfort and appearance.
Antimicrobial finishes are also used in areas such as medical textiles to improve hygiene and safety. Overall, finishing contributes to increasing the value of textiles and makes it possible to optimise them for specific requirements and applications.
Finishing process: Water repellent treatment, anti-crease and anti-pilling finish.
Advantages: Increased durability and comfort.
Special applications: Antimicrobial finishes increase hygiene and are suitable for medical textiles.
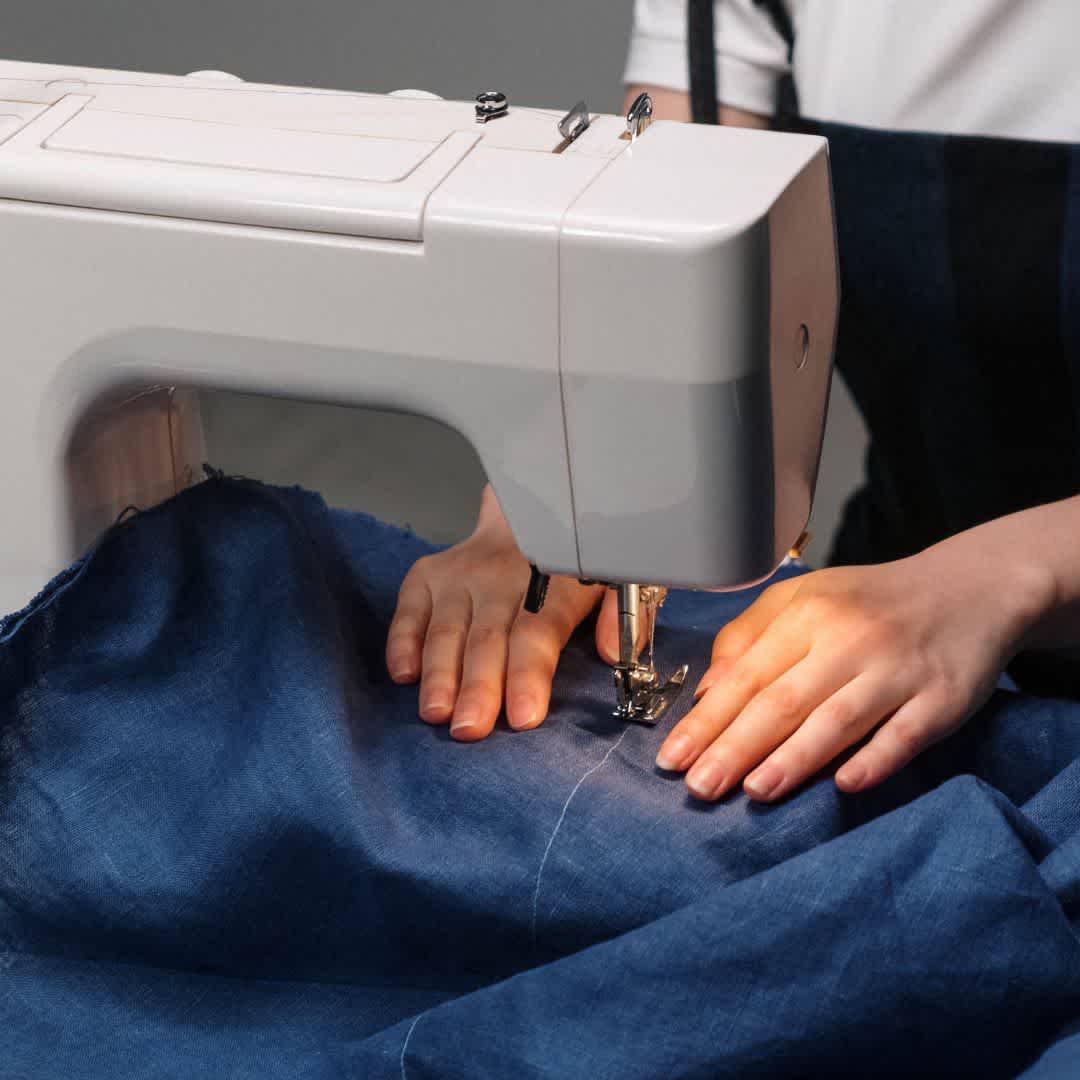
7. sewing
Sewing is the process of assembling the individual pieces of fabric into a finished product. The quality of the seams and the precision of the sewing process are crucial for the stability and appearance of the finished product.
Textile machines such as the overlock and coverstitch make it possible to create stable and even seams that extend the life of the clothing. In addition, techniques such as double or reinforced seams give textile products additional strength, which is particularly relevant for functional and robust workwear.
Quality factors: stitch length, thread quality and precision.
Important machines: overlock, coverstitch and sewing machine.
Reinforcement techniques: Double stitching and special stitches increase the stability and durability of the seams.
8. coating
Coating gives textiles functional properties that are particularly important for outdoor clothing and protective textiles. Fabrics are given special PVC or polyurethane coatings that make them waterproof and weatherproof or increase their abrasion resistance.
In order to reduce the environmental impact, more environmentally friendly alternatives to PVC coatings are increasingly being used. Ultimately, the coated fabrics are essential for functional clothing in particular, which is intended to protect the wearer from extreme weather conditions and mechanical stress.
Applications: Outdoor clothing, workwear and protective clothing.
Coating materials: PVC and polyurethane.
Environmental protection: As they are less harmful to the environment, PVC-free coatings are becoming increasingly popular.
9. laminating
During lamination, several layers of fabric are bonded together to increase the durability and insulating properties of the material. This is particularly relevant in the production of technical textiles that need to have specific properties such as moisture regulation and heat retention.
Laminated fabrics are used in sports and outdoor clothing as well as in protective textiles and are characterised by their high functionality and comfort. Breathable membranes are often integrated into the laminate to increase wearer comfort.
Applications: Sportswear, outdoor textiles and protective textiles.
Advantages: Increased functionality and wearer comfort.
High-performance materials: Laminated textiles are often combined with breathable membranes to provide protection and comfort at the same time.
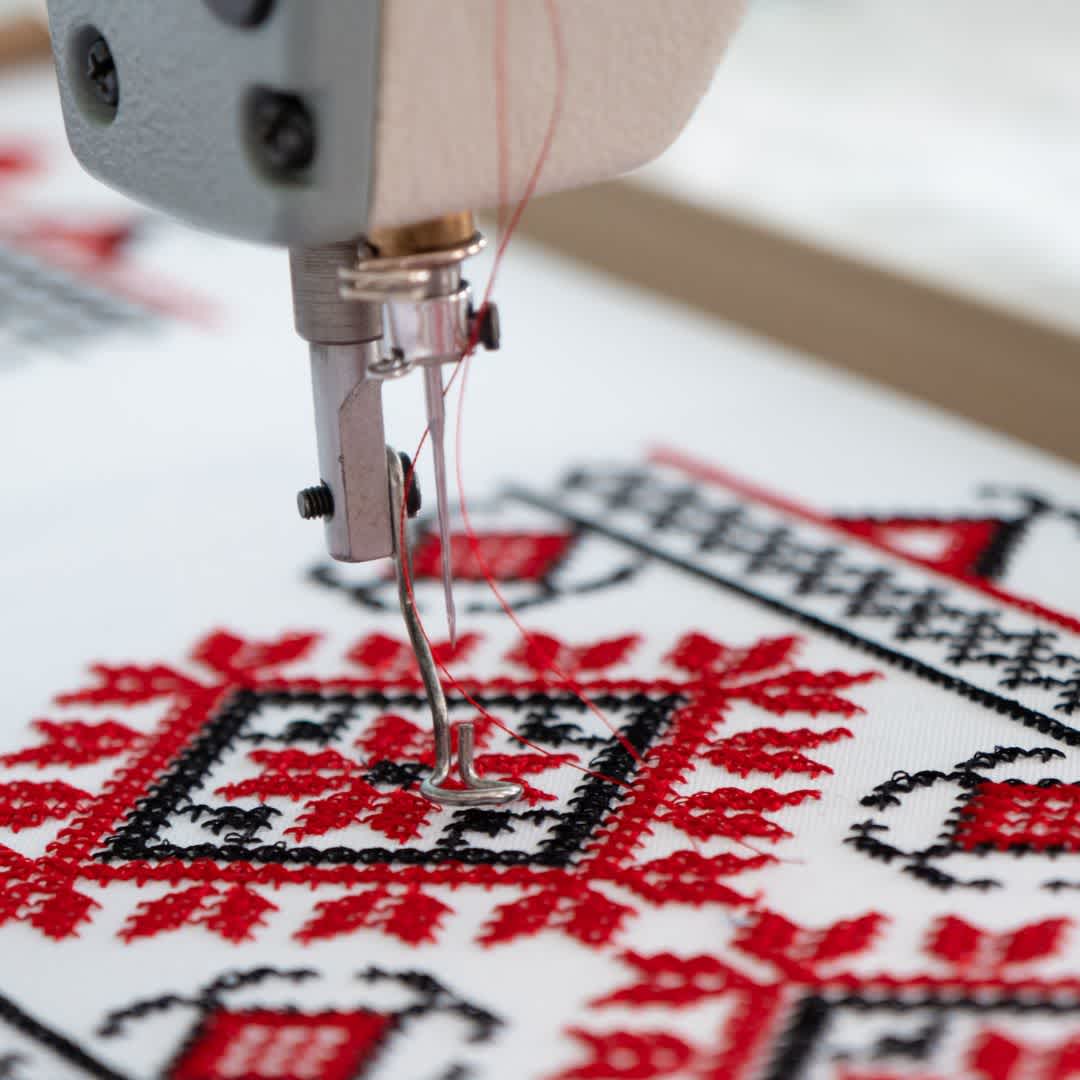
10. embroidery
Embroidery can be used to embellish textiles and add decorative patterns. The process is often used in fashion, home textiles or accessories to create individualised and high-quality designs. Embroidery can be carried out both manually and by machine, with the latter being faster and more precise. Thanks to the possibility of creating unique designs, embroidery is particularly valuable for fashion labels that focus on individualisation and uniqueness.
Process: Hand embroidery and machine embroidery.
Areas of application: Fashion, home décor and accessories.
Individualisation: Embroidery enables unique designs and creates a high-quality look that can individualise textiles.

11. felting
In felting, fibres are compressed under pressure, moisture and heat to create a dense, compact fabric. And because felt can be made from renewable and biodegradable resources such as wool, the process is considered particularly environmentally friendly in textile production.
Felt has naturally insulating properties, which makes it ideal for applications where warmth and protection are required - for example in the manufacture of protective equipment, hats, bags or insulating home textiles.
Applications: Hats, bags and home textiles.
Quality: density and strength of the felt.
Advantage of natural materials: Felt is biodegradable and is often made from renewable fibres such as wool.
Digitalisation in the textile industry
In a modern textile company, advanced production techniques are used to meet the demands of the fashion and textile industry. Innovative technologies such as digital printing and digital control systems are key issues that not only make textile production more environmentally friendly, but also more efficient.
Digitalisation allows many of the traditional production processes mentioned to be optimised and made more transparent. Automated textile machines are indispensable in today's textile production as they increase efficiency and precision. For example, the use of AI-supported systems enables more precise control of the machines, thereby reducing material consumption and increasing production quality.
The benefits of digitalisation also extend to quality assurance and logistics: automated quality control systems supported by machine learning can detect and correct errors or irregularities at an early stage. In addition, the digital tracking of supply chains makes it easier to keep track of resources, origin and production of individual components, which is particularly important in sustainable textile production.
How Line Up optimises textile production
Would you like to have clothing and textiles produced? Our roots lie in the clothing industry. And even today we still produce fabrics, textile accessories and garments with all the functions and refinements of the highest quality.
We offer customised solutions for women's outerwear, workwear, towels and accessories, fabrics, baseball caps and hats, furniture covers, socks with specific technical requirements and much more.
With our comprehensive supplier and production network, we guarantee a seamless service that fulfils all requirements along the entire production chain - from planning and selecting the right process to quality control and logistics.
Newsletter Registration
Sign up now for our free Line Up newsletter and stay up to date.





